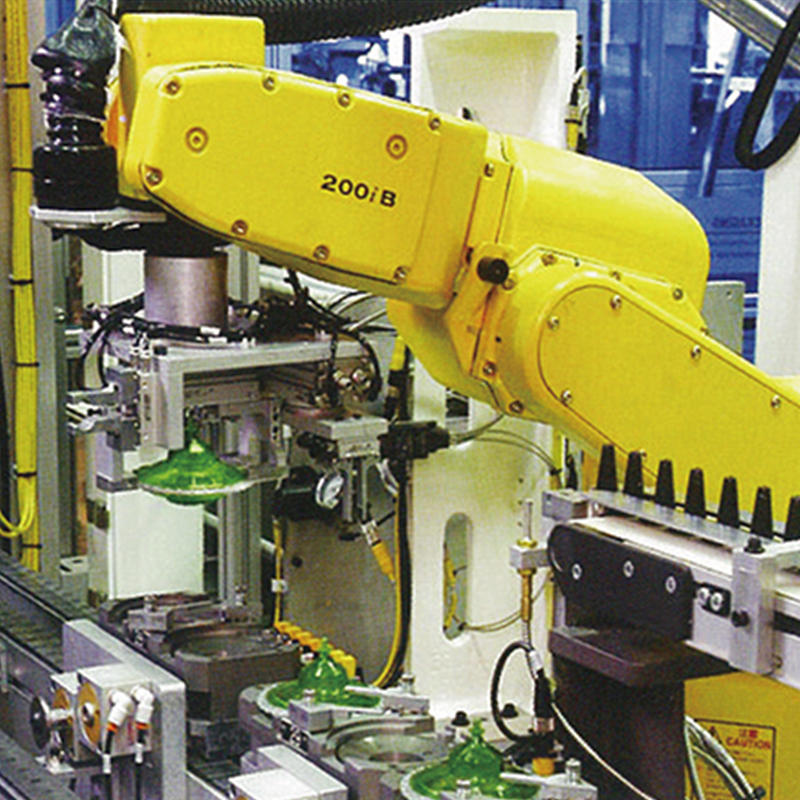
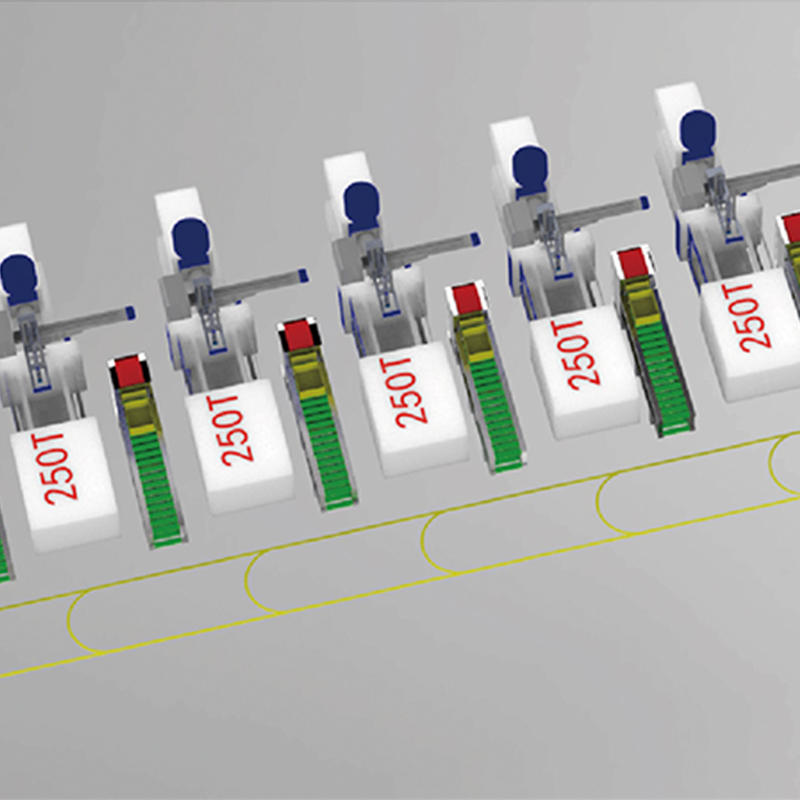
The welding industry has been rapidly evolving with the advent of advanced robotics and automation technologies. Welding robots have become an integral part of modern manufacturing processes, offering numerous benefits such as increased productivity, improved quality, and enhanced safety.
Autonomous welding robots are designed to operate independently, without the need for human intervention. These robots are equipped with advanced sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms that enable them to perceive their environment, make decisions, and execute complex welding tasks.
- High-level programming: Autonomous welding robots can be programmed with specific welding procedures, allowing them to perform a wide range of tasks with small human input.
- Adaptive control: These robots can adapt to changes in the welding environment, such as variations in material thickness or joint configurations, ensuring consistent and high-quality welds.
- Real-time monitoring: Autonomous welding robots can monitor their own performance, detecting and correcting any deviations from the desired welding parameters.
- Large-scale manufacturing: Autonomous welding robots are ideal for high-volume production environments, where consistency and repeatability are crucial.
- Complex geometries: These robots can handle intricate welding tasks that may be difficult or time-consuming for human welders.
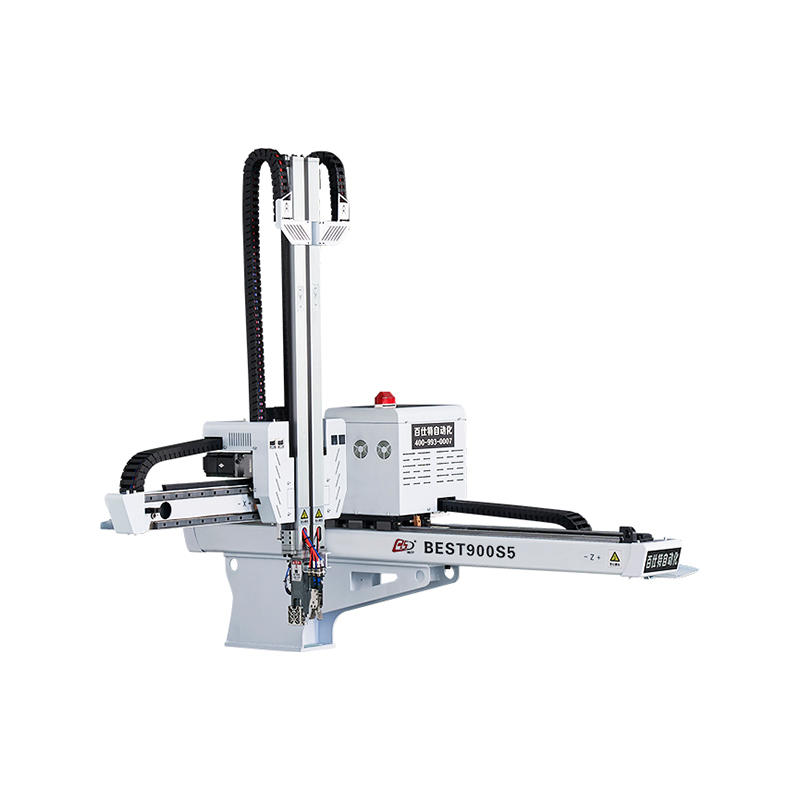
Mobile welding robots are designed to move around the workspace, providing greater flexibility and accessibility compared to their stationary counterparts. These robots are mounted on mobile platforms, such as wheels or tracks, allowing them to navigate various terrains and reach hard-to-access areas.
- Mobility: Mobile welding robots can move freely within their designated workspace, enabling them to perform welding tasks in different locations without the need for repositioning or reprogramming.
- Portability: These robots are designed to be easily transported and set up, making them suitable for a wide range of applications and environments.
- Collision avoidance: Mobile welding robots are equipped with sensors and AI algorithms that help them avoid collisions with obstacles or other robots in the workspace.
- Construction sites: Mobile welding robots can be used in construction environments, where they can navigate uneven terrain and perform welding tasks in hard-to-reach areas.
- Shipbuilding: In shipbuilding, mobile welding robots can move along the length of a ship's hull, performing welding tasks in various locations without the need for repositioning.
Welding cell robots are designed to work within a confined space or a specific area, known as a welding cell. These robots are typically integrated into a larger manufacturing system, where they work in conjunction with other machines and robots to perform a specific set of welding tasks.
- Precision: Welding cell robots are highly accurate, ensuring consistent and high-quality welds within their designated workspace.
- Integration: These robots can be easily integrated into existing manufacturing systems, allowing for seamless coordination with other machines and processes.
- Customization: Welding cell robots can be customized to perform specific welding tasks, such as TIG, MIG, or plasma welding, depending on the requirements of the manufacturing process.
- Automotive manufacturing: Welding cell robots are commonly used in the automotive industry for tasks such as welding car body panels, chassis, and other structural components.
- Aerospace manufacturing: In the aerospace industry, welding cell robots can be used to perform precise welding tasks on complex components, such as aircraft wings and fuselage structures.
The development of autonomous, mobile, and welding cell robots has revolutionized the welding industry, offering numerous benefits in terms of productivity, quality, and safety.



 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى